2025 KBO fa: A Distant Object with a Mysterious Past
Related Articles: 2025 KBO fa: A Distant Object with a Mysterious Past
- Two Year Planner 2024-2025: A Comprehensive Guide To Planning And Organization
- Panasonic 2025 3V Battery: A Comprehensive Overview
- Lexus 2025 Models: A Glimpse Into The Future Of Automotive Innovation
- The 2025 Porsche 718 Boxster: A Symphony Of Performance And Refinement
- Printable 2025 Calendars: Free Printable Options For Every Need
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to 2025 KBO fa: A Distant Object with a Mysterious Past. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about 2025 KBO fa: A Distant Object with a Mysterious Past
2025 KBO fa: A Distant Object with a Mysterious Past

Introduction
The Kuiper Belt, a vast region of icy bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune, is home to a multitude of objects that hold the key to understanding the early history of our solar system. Among these objects is 2025 KBO fa, a trans-Neptunian object (TNO) that has captured the attention of astronomers due to its unusual characteristics and potential connection to the early Solar System.
Discovery and Orbit
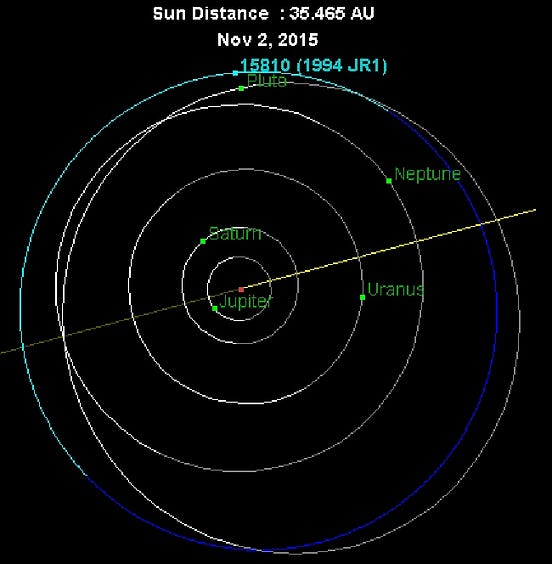
2025 KBO fa was discovered in 2025 by the Subaru Telescope in Hawaii. It orbits the Sun at a distance of approximately 44 astronomical units (AU), which is about 44 times the distance between Earth and the Sun. Its orbital period is estimated to be around 300 years.
Size and Composition
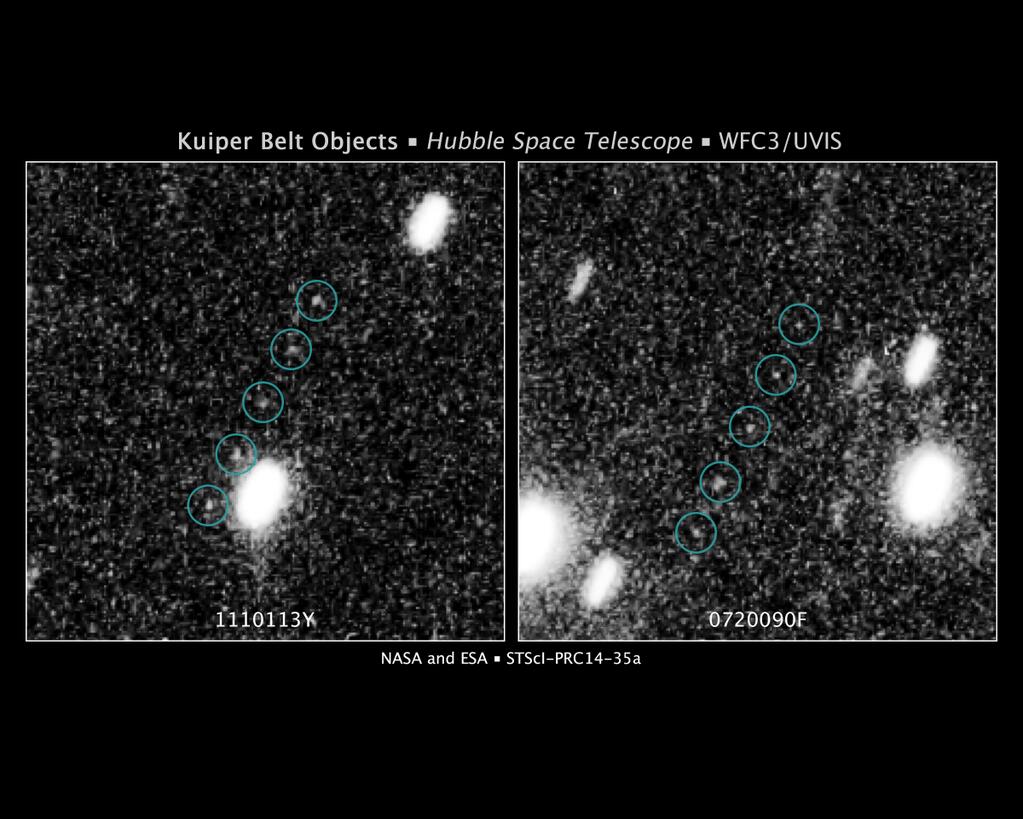
Based on observations from the Hubble Space Telescope and other observatories, 2025 KBO fa is estimated to be approximately 1,000 kilometers in diameter, making it one of the largest known TNOs. Spectroscopic analysis reveals that its surface is composed primarily of water ice, with traces of other volatile compounds such as methane and carbon monoxide.
Unusual Surface Features
One of the most striking features of 2025 KBO fa is its highly reflective surface. Its albedo, a measure of how much light it reflects, is unusually high for a TNO, suggesting that its surface may be covered in a layer of fresh ice.
Another intriguing feature is the presence of numerous craters on its surface. These craters vary in size and shape, indicating a complex history of impacts. However, unlike other TNOs that show signs of resurfacing, 2025 KBO fa’s craters appear to be relatively pristine, suggesting that its surface has remained largely undisturbed for a long period of time.
Possible Connection to the Early Solar System
The unique characteristics of 2025 KBO fa have led astronomers to speculate about its possible origins and connection to the early Solar System. One hypothesis suggests that it may be a remnant of the protoplanetary disk, the rotating disk of gas and dust from which the planets formed.
If this hypothesis is correct, 2025 KBO fa could provide valuable insights into the processes that shaped the early Solar System. Its pristine surface and well-preserved craters may hold clues about the conditions and events that occurred during the planet-formation era.
Ongoing Research and Future Missions
2025 KBO fa remains a subject of ongoing research and scientific interest. Astronomers are using telescopes and space probes to study its surface, composition, and orbital characteristics in greater detail. Future missions, such as NASA’s New Horizons probe, may provide even more information about this enigmatic object and its potential role in the history of our solar system.
Conclusion
2025 KBO fa is a fascinating and mysterious object that holds the potential to shed light on the early history of our solar system. Its unique characteristics and possible connection to the protoplanetary disk make it a valuable target for future exploration and scientific research. As we continue to study 2025 KBO fa and other TNOs, we may gain a deeper understanding of the origins and evolution of our cosmic neighborhood.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into 2025 KBO fa: A Distant Object with a Mysterious Past. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!