How Does an Internal Combustion Engine Work?
Related Articles: How Does an Internal Combustion Engine Work?
- Google Price Prediction 2025: A Comprehensive Analysis
- 2024 Vs 2025 Equinox: A Comprehensive Comparison
- 2025 Chevy Equinox: A Fuel-Efficient SUV With Enhanced Performance
- Quarterbacks To Watch For The 2024 NFL Draft
- Lethal Weapon 5: A Legacy Revived (2025)
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to How Does an Internal Combustion Engine Work?. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about How Does an Internal Combustion Engine Work?
How Does an Internal Combustion Engine Work?
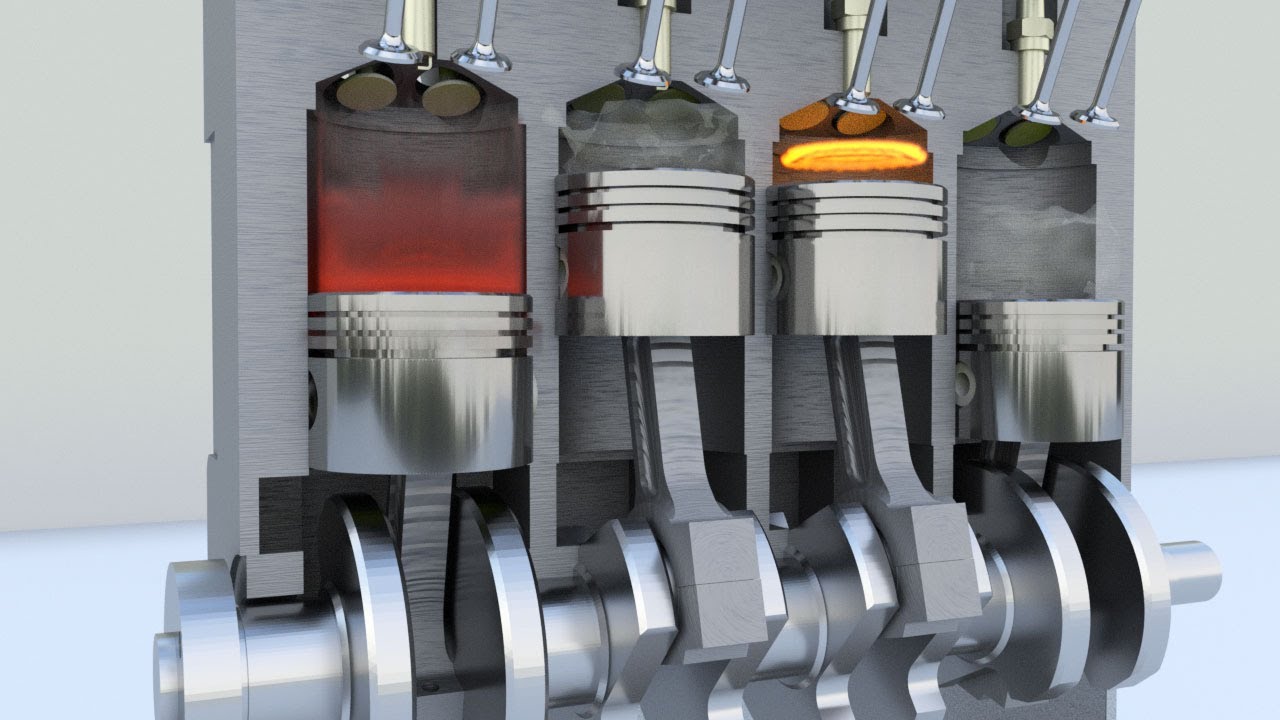
An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine that uses the expansion of hot gases to produce mechanical work. It is the most common type of engine used in vehicles, such as cars, trucks, and motorcycles.
ICEs operate on the principle of burning fuel inside a cylinder, which causes the gases to expand and push a piston. The piston is connected to a crankshaft, which converts the linear motion of the piston into rotary motion. The crankshaft is then connected to the transmission, which sends power to the wheels.
There are two main types of ICEs: spark-ignition (SI) engines and compression-ignition (CI) engines. SI engines use a spark plug to ignite the fuel-air mixture, while CI engines use the heat of compression to ignite the fuel.
Spark-Ignition Engines
SI engines are the most common type of ICE used in vehicles. They are typically used in gasoline-powered vehicles.
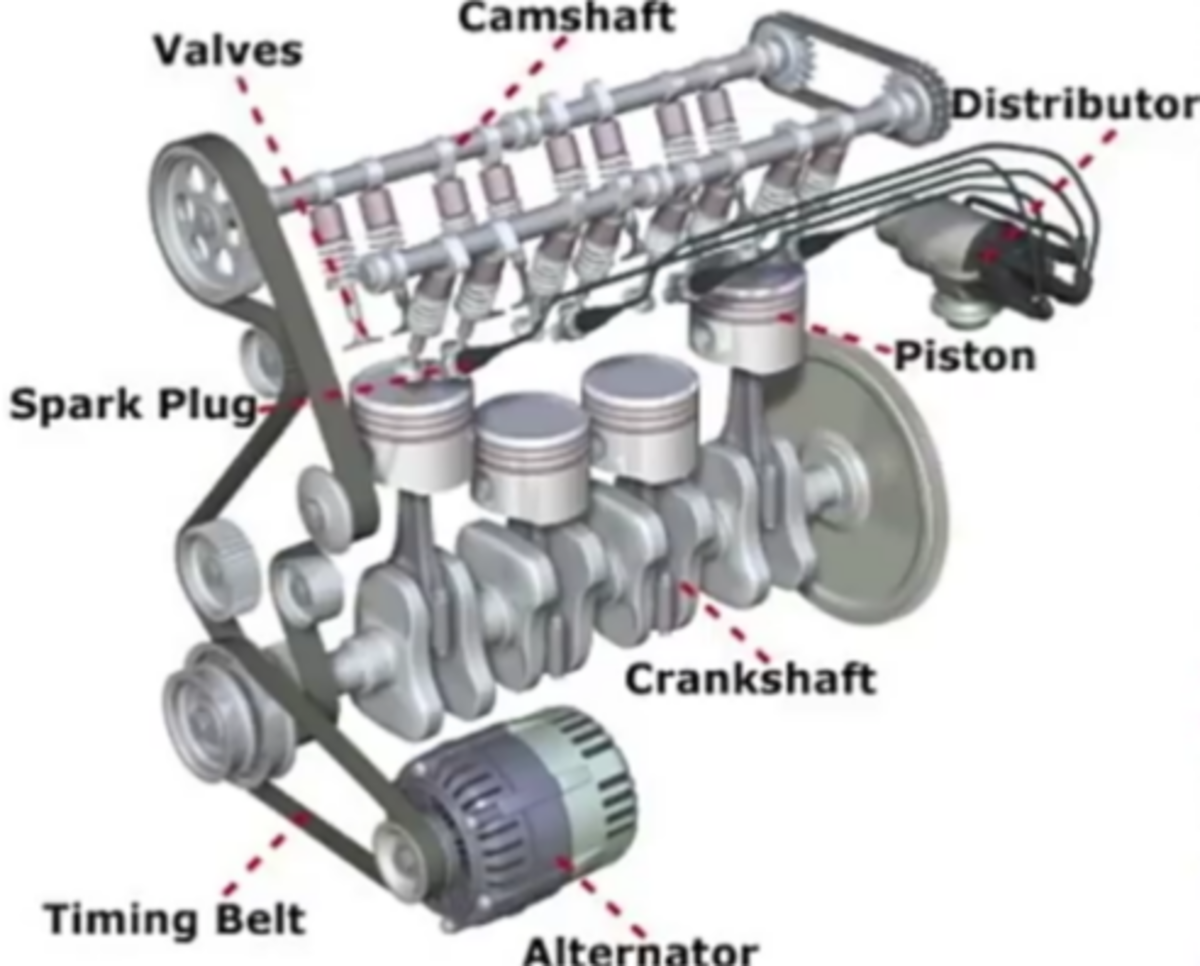
The basic components of an SI engine are:
- Cylinders: The cylinders are where the fuel-air mixture is burned.
- Pistons: The pistons move up and down inside the cylinders, compressing the fuel-air mixture and pushing it out of the cylinders.
- Crankshaft: The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotary motion.
- Valves: The valves control the flow of air and fuel into and out of the cylinders.
- Spark plugs: The spark plugs ignite the fuel-air mixture.
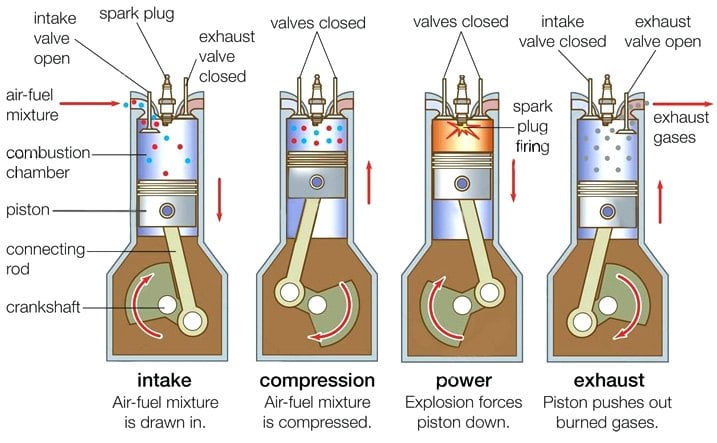
The operation of an SI engine is as follows:
- The intake valve opens, allowing air and fuel to enter the cylinder.
- The piston moves up, compressing the air and fuel mixture.
- The spark plug ignites the air and fuel mixture.
- The expanding gases push the piston down, creating power.
- The exhaust valve opens, allowing the exhaust gases to escape from the cylinder.
Compression-Ignition Engines
CI engines are typically used in diesel-powered vehicles. They are more efficient than SI engines, but they produce more emissions.
The basic components of a CI engine are:
- Cylinders: The cylinders are where the fuel-air mixture is burned.
- Pistons: The pistons move up and down inside the cylinders, compressing the air and fuel mixture and pushing it out of the cylinders.
- Crankshaft: The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotary motion.
- Valves: The valves control the flow of air and fuel into and out of the cylinders.
- Fuel injectors: The fuel injectors spray fuel into the cylinders.
The operation of a CI engine is as follows:
- The intake valve opens, allowing air to enter the cylinder.
- The piston moves up, compressing the air.
- The fuel injector sprays fuel into the cylinder.
- The heat of compression ignites the fuel.
- The expanding gases push the piston down, creating power.
- The exhaust valve opens, allowing the exhaust gases to escape from the cylinder.
Advantages of ICEs
ICEs are a well-established technology that is relatively inexpensive to produce. They are also relatively efficient, and they can run on a variety of fuels, including gasoline, diesel, and natural gas.
Disadvantages of ICEs
ICEs produce emissions that can contribute to air pollution and climate change. They are also relatively noisy, and they can require a lot of maintenance.
The Future of ICEs
The future of ICEs is uncertain. As the world moves towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, ICEs are likely to be phased out in favor of electric vehicles and other alternative fuel vehicles. However, ICEs are still likely to be used in some applications, such as long-haul trucking and heavy equipment.
Conclusion
ICEs are a versatile and efficient type of engine that has been used in vehicles for over a century. However, they are also a major source of emissions, and they are likely to be phased out in favor of cleaner and more sustainable energy sources in the future.
.png)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into How Does an Internal Combustion Engine Work?. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
